Introduction
Monitoring network traffic is essential for diagnosing performance issues, optimizing bandwidth, and ensuring server reliability. nload is a lightweight, command-line tool that provides real-time insights into your network interfaces’ upload and download speeds. Whether you’re managing a server, troubleshooting connectivity, or simply curious about network activity, this guide will walk you through installing and using nload on AlmaLinux 8 or 9.
What is nload?
nload is a terminal-based utility that displays incoming and outgoing network traffic in real-time. Key features include:
- Live Graphs: Visualize traffic with dynamic ASCII charts.
- Multiple Interfaces: Monitor specific or all network interfaces (e.g.,
eth0,wlan0). - Minimal Resource Usage: Lightweight and ideal for servers.
- User-Friendly: No complex setup required.
Prerequisites
- AlmaLinux 8 or 9 installed.
- Terminal access with sudo privileges.
- An active internet connection.
Step 1: Update System Packages
Ensure your system is up-to-date:
sudo dnf update -yStep 2: Enable the EPEL Repository
nload is available in the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository. Enable EPEL:
sudo dnf install epel-release -yStep 3: Install nload
Install the package using dnf:
sudo dnf install nload -yStep 4: Verify Installation
Confirm nload is installed correctly:
nload --version
# Output example: nload 0.7.4Basic Usage of nload
- Monitor All Interfaces:
nload- Use arrow keys to switch interfaces.
- Press q to quit.
- Monitor a Specific Interface (e.g.,
eth0):
nload eth0- Adjust Refresh Interval (e.g., 2 seconds):
nload -t 2000 eth0Understanding the nload Interface
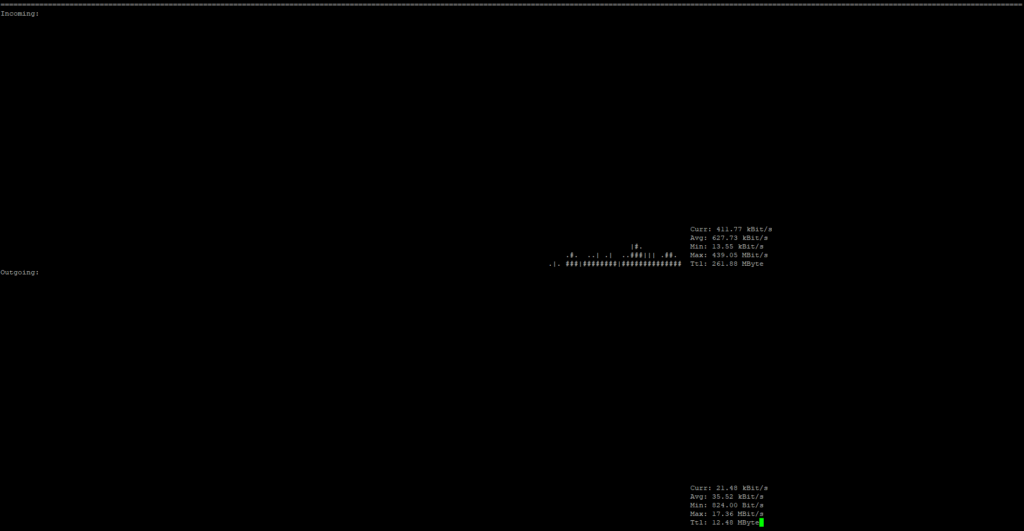
- Incoming Traffic (Incoming): Download speed (e.g.,
Curr: 1.45 Mbit/s). - Outgoing Traffic (Outgoing): Upload speed.
- Graphs: Visualize traffic spikes over time.
- Device: Name of the monitored interface.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. EPEL Repository Not Found
If epel-release fails to install, manually add the EPEL repo:
sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-$(rpm -E %rhel).noarch.rpm -y2. Interface Not Detected
List active interfaces to confirm the correct name (e.g., eth0, enp0s3):
ip a3. Permission Denied
Run nload with sudo if restricted:
sudo nloadUninstalling nload
To remove the tool:
sudo dnf remove nload -yAlternatives to nload
- iftop: Monitor bandwidth per connection.
- vnStat: Track hourly/daily/monthly usage.
- bmon: Advanced interface statistics.
Why Use nload on AlmaLinux?
- Real-Time Insights: Identify bandwidth spikes instantly.
- Server-Friendly: No GUI required—ideal for headless systems.
- Quick Diagnostics: Troubleshoot network issues faster.
Conclusion
nload is a powerful yet simple tool for monitoring network traffic on AlmaLinux 8/9. With just a few commands, you can install it via the EPEL repository and start analyzing bandwidth usage in real-time. Whether you’re optimizing a web server or auditing network performance, nload delivers clarity without complexity.
Alt Text for Images (if added):
“Terminal screenshot showing nload monitoring network traffic on AlmaLinux with live upload/download graphs.”
Need Help?
Optimize your server’s performance today with nload! 🚀🔍

